|
A useful way to express exact concentrations of solutions is
molarity.
Molarity is defined as moles of solute per liter of solution.
Molarity is symbolized by the capital letter M. It can be expressed
mathematically as follows.
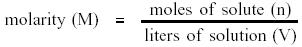
Notice that the moles of solute are divided by the liters of
solution not solvent. One liter of one molar solution will consist of one mole
of solute plus enough solvent to make a final volume of one liter.
Example 1:
Prepare one molar solution of NaCl. Solution:
a)Calculate
the molecular weight of the salt
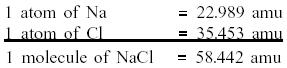
One mole is equal to the gram molecular weight, so one mole
= 58.442 grams.
b) 58.442
grams of NaCl is weighed out and sufficient water is added to bring the
solution to one liter.
Example 2:
Prepare 3 liters of a 2M
NaOH solution.
Solution:
Calculate the amount of
NaOH required to prepare the solution.
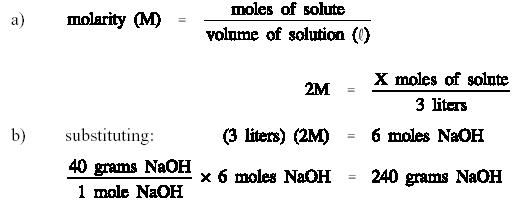
Therefore, to prepare 3
liters of a 2M NaOH solution, 240 grams of NaOH must be weighed out and
dissolved in water to make a volume of exactly 3 liters.
|

