|
Chemicals can be combined with certain metals to cause a
chemical reaction that will transfer electrons to produce electrical energy.
This process works on the electrochemistry
principle. One example of this principle is the voltaic chemical cell,
shown in Figure 11. A chemical reaction produces and maintains opposite charges
on two dissimilar metals that serve as the positive and negative terminals. The
metals are in contact with an electrolyte solution. Connecting together more
than one of these cells will produce a battery.
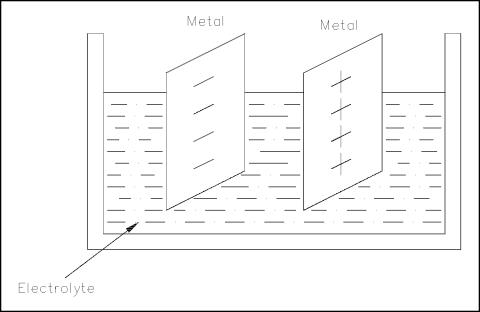
Figure 11 Voltaic
Chemical Cell
Example: A battery can maintain a potential
difference between its positive and negative terminals by chemical action.
Various types of cells and batteries will be studied in more detail in Module 4,
Batteries.
|

