|
Sizing
and selection of lead-acid batteries should be performed according to ANSI/IEEE
Std 485,
IEEE Recommended Practice for Sizing Large Lead Storage Batteries for
Generating Stations and Substations. As described earlier, the duty
cycle is the most important criterion in battery sizing and selection.
ANSI/IEEE Std 485 contains directions as well as a sample exercise for
determining the duty cycle. A simple duty cycle diagram is shown in Figure 15.
Each
of the loads (designated by L1_6)requires a certain amperage for a specified time and duration. In the
example duty cycle, a randomly occurring load (Ir7) is assumed to occur in the 120th minute. The
placement of randomly occurring loads in the duty cycle is also covered in
ANSI/IEEE Std 485.
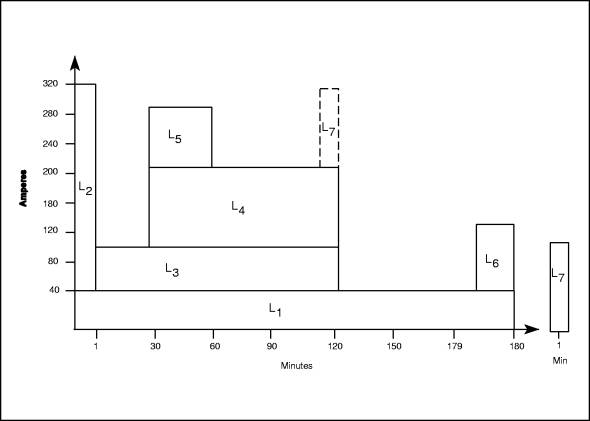
Figure 15. Diagram of a duty cycle.
Other
selection factors recommended by ANSUIEEE Std 485 are the following:
I. Physical characteristics, such as size
and weight of the cells, container material, vent caps, intercell connectors,
and terminals
2. Planned life of the installation and
expected life of the cell design
3. Frequency and depth of discharge
4. Ambient temperature
5. Maintenance requirements for the
various cell designs
6. Seismic characteristics of the cell
design.
Additional
requirements for nuclear facility service are contained in ANSI/IEEE Std 535, IEEE Standard for Qualification of Class 1 E
Lead Storage Batteries for Nuclear Power Generating Substations.
|

