|
This
chapter covers the calculation of the surface area and volume of selected solid
figures.
EO 1.5
Given
the formula, CALCULATE the volume and
surface areas of the following solid figures:
a. Rectangular solid
b.
Cube
c.
Sphere
d. Right circular cone
e. Right circular cylinder
The
three flat shapes of the triangle, rectangle, and circle may become solids by
adding the third dimension of depth. The triangle becomes a cone;
circle,
a cylinder.
the
rectangle, a rectangular solid; and the
Rectangular Solids
A
rectangular solid is a six-sided solid figure with faces that are rectangles, as shown in
Figure 14.
The
volume of a rectangular solid is calculated using the following formula:
V = abc (3-11)
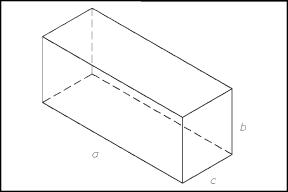
Figure
14 Rectangular Solid
The
surface area of a rectangular solid is calculated using the following formula:
SA =
2(ab + ac + bc) (3-12)
The
surface area of a rectangular solid is expressed in square units, and the
volume of a rectangular solid is expressed in cubic units.
Example:
Calculate
the volume and surface area of a rectangular solid with a = 3", b = 4", and c
= 5". Be sure to include units in your answer.
Solution:
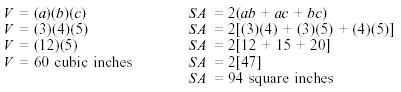
Cube
A cube is a six-sided solid figure whose faces are congruent squares, as shown
in Figure 15.
The
volume of a cube is calculated using the following formula:

The
surface area of a cube is calculated using the following formula:
SA = 6a2 (3-14)
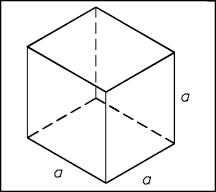
Figure 15 Cube
The
surface area of a cube is expressed in square units, and the volume of a cube
is expressed in cubic units.
Example:
Calculate
the volume and surface area of a cube with a
= 3". Be sure to include units in your answer.
Solution:

|

