|
There are two unit systems in use at the present
time, English units and International System of Units (SI).
In the United States, the English system is
currently used. This system consists of various units for each of the
fundamental dimensions or measurements. These units are shown in Table 1.

The English system is presently used in the field of
engineering and throughout the United States. The foot-pound-second (FPS)
system is the usual unit system used in the U.S. when dealing with physics.
Over the years there have been movements to
standardize units so that all countries, including the United States, will
adopt the SI system. The SI system is made up of two related systems, the
meter-kilogram-second (MKS) system and the centimeter-gram-second (CGS) system.
The MKS and CGS systems are much simpler to use than
the English system because they use a decimal-based system in which prefixes
are used to denote powers of ten. For example, one kilometer is 1000 meters,
and one centimeter is one one-hundredth of a meter. The English system has odd
units of conversion. For example, a mile is 5280 feet, and an inch is one
twelfth of a foot.
The MKS system is used primarily for calculations in
the field of physics while both the MKS and CGS systems are used in the field
of chemistry. The units for each of these systems are shown in Tables 2 and 3
below.
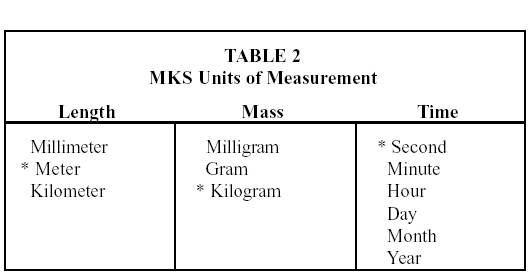
* Standard
unit of measure

* Standard
unit of measure
The following tables show
approximate lengths, masses, and times for some familiar objects or events.



|

