|
FUNCTIONS AND COFUNCTIONS The functions cosine, cosecant, and cotangent
are cofunctions of the functions sine, secant, and
tangent, respectively. A cofunction of an angle
A has the same value as the corresponding
function of (90 A); that is, the same value as
the corresponding function of the complement of
the angle. The sine of 30, for example, is
0.50000. The cosine of 60 (the complement of
30) is likewise 0.50000. The tangent of 30 is
0.57735. The cotangent of 60 (the complement of 30) is likewise 0.57735.
Commonly used functions and cofunctions are as follows:
sin A = cos (90 A)
sec A = csc (90 A)
tan A = cot (90 A)
FUNCTIONS OF
OBTUSE ANGLES
In figure 1-22, the point P has generated an
obtuse (larger than 90) angle of 135. This angle
is the supplement of 45 (two angles are
supplementary when they total 180). We have
left a dotted image of the reference angle A, which
is equal to the supplementary angle of 135. You
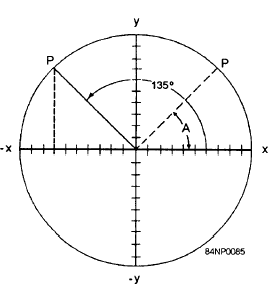
Figure 1-22.-Function of an obtuse angle.
can see that the values of x, y, and r are the same for
135 as they are for 45, except that the value of x is
negative. From this it follows that the functions of any
obtuse angle are the same as the functions of its
supplement, except that any function in which x appears
has the opposite sign.
The sine of an angle is y/r. Since x does not appear
in this function, it follows that sin A = sin (180 A).
The cosine of an angle is fir. Since x appears in this
function, it follows that cos A = - cos (180 A).
The tangent of an angle is y/x. Since x appears in
this function, it follows that tan A = tan ( 180- A).
The importance of knowing this lies in the fact that
many tables of trigonometric functions list the functions
only for angles to a maximum of 90. Many oblique
triangles, however, contain angles larger than 90. To
determine a function of an angle larger than 90 from a
table that stops at 90, you lookup the function of the
supplement of the angle. If the function is a sine, you
use it as is. If it is a cosine or tangent, you give it a
negative sign.
The relationships of the function of obtuse angles
are as follows:
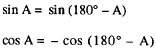
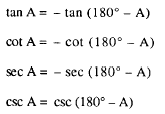
The above relationships apply only when angle A
is greater than 90 and less than 180.
|







