|
SKETCHING MATERIALS One of the main advantages of sketching is that
few materials are required. Basically, you need
only a pencil and paper. However, the type of
sketch prepared and your personal preference will
determine the materials used.
You should use a soft pencil in the grade range from
F to 3H, with H being a good grade for most sketching.
The pencil should be long enough to permit
a relaxed but stable grip. As you gain experience,
you may even prefer to use fine tip felt
pens. (Dark- or bright-colored pens should be
used.) Felt tip pens work very well on overlay sketches
(discussed later).
Most of your sketches will be done on scratch paper,
which can be any type or size of paper. An
experienced draftsman will keep a pad of 3 in. by
5 in. or 5 in. by 8 in. scratch paper handy at all
times. For planning the layout of a drawing,
you will find tracing paper to be convenient.
The advantage of sketching on tracing
paper is the ease with which sketches can
be modified or redeveloped simply by placing
transparent paper over previous sketches or
existing drawings. Sketches prepared in this
manner are referred to as OVERLAY SKETCHES.
Cross-section or graph paper may be
used to save time when you are required to draw
sketches to scale. (See fig. 5-56.) Isometric sketches
are easily done on specially ruled isometric
paper. (See fig. 5-57.)
An eraser maybe used, but you will probably do
very little erasing. Sketches usually can be
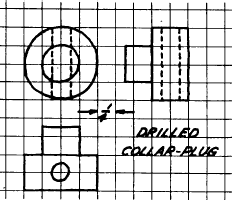
Figure 5-56.-Use of cross-sectional paper in technical sketching.
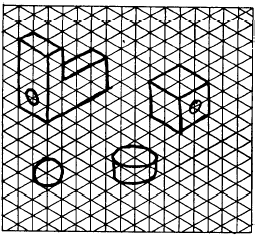
Figure 5-57.-Use of specially ruled isometric paper in technical
sketching.
redrawn more quickly than mistakes can be erased.
For making dimensioned sketches in the field, you
will need some sort of measuring tapeeither a
pocket rule or a surveyors tape, depending on the
extent of the measurements taken. If you are required
to collect extensive field data, it would be
to your benefit to maintain a sketch notebook. A
surveyors field notebook works well for this purpose.
|

