ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q1. THROUGH Q43.
A1. Transformer, rectifier, filter, regulator.
A2. To change ac to pulsating dc.
A3. To change pulsating dc to pure dc.
A4. To maintain a constant voltage to the load.
A5. The half-wave rectifier.
A6. 15.9 volts.
A7. It isolates the chassis from the power line.
A8. The fact that the full-wave rectifier uses the full output, both half cycles, of the
transformer.
A9. 120 hertz.
A10. 63.7 volts.
A11. Peak voltage is half that of the half-wave rectifier.
A12. The bridge rectifier can produce twice the voltage with the same size transformer.
A13. It will decrease. Capacitance is inversely proportional to:
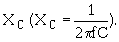
A14. The capacitor filter.
A15. Parallel.
A16. At a high frequency.
A17. A filter circuit increases the average output voltage.
A18. Value of capacitance and load resistance.
A19. Good.
A20. Yes.
A21. The CEMF of the inductor.
A22. From 1 to 20 henries.
A23. Decrease.
A24. Expense.
A25. When ripple must be held at an absolute minimum.
A26. LC capacitor-input filter.
A27. Cost and size of the inductor.
A28. Regulators.
A29. Variation.
A30. Series and shunt.
A31. An increase.
A32. In parallel.
A33. Bias.
A34. Increases.
A35. Increases.
A36. Decreases.
A37. An increase.
A38. Two.
A39. Trippler.
A40. In parallel.
A41. Safety precautions.
A42. To eliminate shock hazard.
A43. Visual and signal tracing.




