|
Scale
and Distance A map
is a graphic representation of an area and, therefore, is not made to full
scale (actual size). Since it is not full size, some means of measuring the
distance from one point on the map to another is necessary. This is done with
the aid of a scale.
There
are two types of scales in general use on military maps. The first is called a
graphic scale and is
Figure
5-20.-Measuring curved line distance on a map.
indicated
by a special scale legend that is printed on the map. The second type of scale
is the ratio between the horizontal distance on the map and the corresponding
distance on the ground.
The
GRAPHIC SCALE that is printed on your map is especially made for that map and
should not be used on any other map. Figure 5-19 shows a typical graphic scale.
To the right of the zero (0), the scale is marked in full units of measure and
is called the PRIMARY SCALE. The part to the left is zero (0) and is divided
into tenths of a unit and is called the EXTENSION SCALE. Most maps have three
or more graphic scales, each of which indicates distance in a different unit of
measure. To determine the straight-line distance between two points on a map,
use the following steps:
1.
Lay the straightedge of a piece of paper on the map so the edge of the paper
touches both points.
2.
Make a mark on the edge of the paper at each point.
3.
Move the paper down to the graphic scale, and from the scale, read the ground
distance between the points. Be sure to use the scale that indicates the unit
of measure desired.
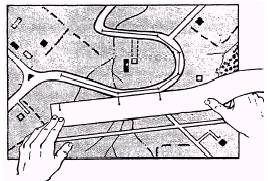
To
measure distance along a winding road, stream, or other curved line, the
straightedge of a piece of paper should be used again.
1.
Make a mark at or near one end of the paper and place it at the point from
which the line is to be measured, as shown in figure 5-20.
2. Align
the edge of the paper along a straight portion, and make a tick mark on both
the map and the paper at the end of the aligned portion
3.
Keeping both tick marks together, place the point of the pencil on the tick
mark of the paper to hold it in place. Pivot the paper until another straight
portion is aligned and make another mark on both map and paper.
4.
Continue in this manner until the measurement is complete. Then place the paper
on the graphic scale and read the ground distance.
The
RATIO-TYPE SCALE is simply a comparison between a given distance measured on
the map and on the ground. It is independent of any unit of measure. A scale of
1/25,000 means that one unit of measure on the map is equal to 25,000 of the
same units of measure on the ground. The ground distance between two points may
be determined by measuring between the points on the map and multiplying the
map measurement by the scale. For example, the distance between two bridges on
a certain map is 15 inches. The scale of the map is 1:50,000. Therefore, the
actual distance on the ground is found by multiplying 15 inches by 50,000 (15
times 50,000 equals 750,000 inches). If this is to mean anything to you, change
it to units that can be easily pictured in your mind. These units might be feet,
yards, meters, kilometers, or miles. To change the 750,000 inches to feet, you
need to divide by 12 (the number of inches in a foot); hence 750,000 divided by
12 equals 62,500 feet. To change the 62,500 feet to miles, divide again by
5,280 (the number of feet per mile); thus 62,500 divided by 5,280 equals 11.8
miles.
By
using either of the methods described above, you can determine the distance
between any two points.
|

