|
FOOTING AND FOOTING REINFORCE-MENT. Footings support the entire structure and
distribute the load to the ground. The size and
shape of a footing depend upon the design of
the structure. In a small footing (fig. 7-2), "steel
mats" or reinforcements are generally preassembled
and placed after the forms have been
set. In large or continuous footings, such as those
found under bearing walls, steel mats are constructed
in place.
COLUMN AND COLUMN REINFORCE-MENT.
A column is a slender, vertical member that
carries a superimposed load. Concrete columns,
especially those subjected to bending stresses,
must always be reinforced with steel. A PIER
or PEDESTAL is a compressive member that
is short (usually the height is less than three times
the least lateral dimension) in relation to its cross-sectional
area and carries no bending stress. In
concrete columns, vertical reinforcement is the
principal reinforcement. However, a loaded column
shortens vertically and expands laterally; hence,
lateral reinforcements in the form of lateral ties
are used to restrain the expansion. Columns reinforced
in this manner are called tied columns (fig.
7-3, view A). If the restraining reinforcement is
a continuous winding spiral that encircles the core
and longitudinal steel, the column is called a
spiral column (fig, 7-3, view B).
BEAM AND BEAM REINFORCE-MENT.
Beams are the principal load-carrying horizontal
members. They take the load directly from
the floor and carry it to the columns. Concrete
beams can either be cast in place or precast
and transported to the jobsite. Figure 7-4 shows
several common types of beam reinforcing steel
shapes. Both straight and bent-up principal
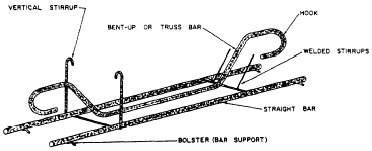
Figure 7-4.-Typica1 shapes of
reinforcing steel.
reinforcing bars are needed to resist the bending tension
in the bottom over the central portion of the
span. Fewer bars are necessary on the bottom near
the ends of the span where the bending moment
is small. For this reason, some bars may be
bent so that the inclined portion can be used to
resist diagonal tension. The reinforcing bars of
continuous beams are continued across the supports
to resist tension in the top in that area.
|

|

