

Custom Search
|
|
 
|
||
|
ALGEBRAIC NOTATION AND
ALGEBRAIC OPERATIONS Algebraic notationmeaning generally the substitution of symbols (usually letters) for numerical values-is explained in chapter 9 of NAVEDTRA 10069-D1. Algebraic fundamentals, such as the meanings of terms; systems of groupings; and the addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of algebraic monomials and polynomials are explained in the same chapter. The factoring of algebraic expressions is explained in chapter 10. GEOMETRY Since geometry is the branch of mathematics that investigates the relations, properties, and measurement of solids, surfaces, lines, and angles, it follows that just about everything a surveyor does involves geometry in some way or other. Whenever you establish a point, chain a linear distance, measure a vertical distance, turn an angle, or determine an area or a volume, you are working with geometry. To begin with, you must know how to recognize the common types of geometrical plane and solid figures and how to compute the areas of the plane figures and the volumes of the solids. SURFACES AND FIGURES There is a surface on this sheet of paper. A geometrical surface has length and breadth. It has 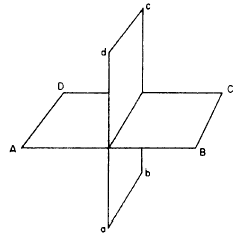
Figure 1-3.-Intersecting planes. no thickness. A surface may be either a plane surface or a curved surface. When this page is held perfectly level at every point, the surface is then a plane surface. When the page is rolled to resemble a tube, the plane surface becomes a curved surface. A plane is a real or imaginary surface in which a straight line between any two points lies wholly on that surface. Figure 1-3 shows two intersecting planes. Plane ABCD is shown to be a horizontal plane; plane abed is a vertical plane perpendicular to ABCD. A plane surface is a surface on which every point lies in the same plane. Plane figures are plane surfaces bounded by either straight lines or curved lines. A plane figure that is bounded by straight-line sides is called a polygon. The smallest possible number of sides for a polygon is three, and a three-sided polygon is called a triangle. Some terms and definitions relating to polygons are as follows: Sides The boundary lines of a polygonPerimeter The sum of the sides
A triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, heptagon, and octagon are shown in figure 1-4. A trapezoid, trapezium, rhombus, and rhomboid are shown in figure 1-5. |
 
|
|
  |
||